Description
- As we know the ESP-NOW is a wireless communication protocol developed by Espressif Systems for its Wi-Fi chips.
- It allows devices to communicate directly with each other without the need for a Wi-Fi access point.
- Here In this guide, we will send the temperature and humidity data from the master device to many other devices.
- We will be using two ESP32 boards and one NodeMCU board, the DHT11 sensor is connected to one ESP32 and another ESP32 and NodeMCU will become a slave.
.png)
Before going forward we need to have a minimum of two ESP32/NodeMCU boards and know the MAC address of its.
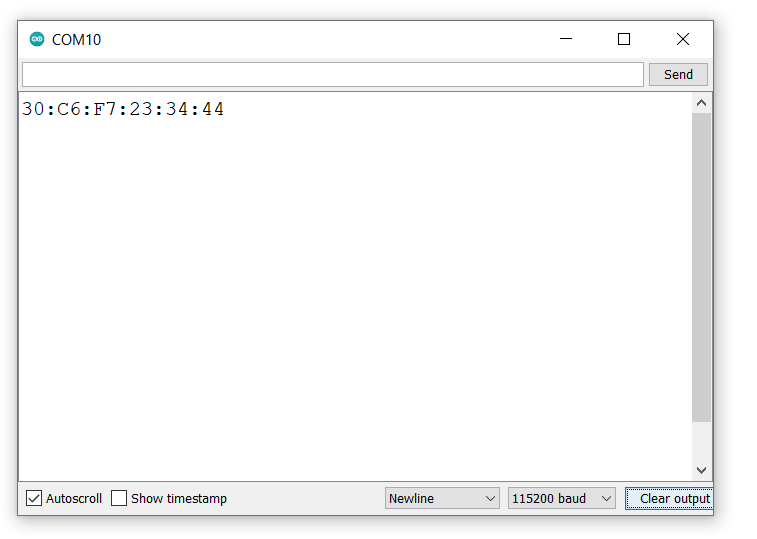
So first get the MAC address from the below code and note down it.
Getting Board MAC Address
#ifdef ESP32
#include <WiFi.h>
#else
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#endif
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println();
Serial.println(WiFi.macAddress());
}
void loop(){}
Output
Connection Diagram of DHT11 with ESP32
.png)
Now copy the below code and upload it on the first esp32 device. Before uploading you must have to enter the MAC address of your slave device
uint8_t broadcastAddress1[] = {0x30, 0xC6, 0xF7, 0x23, 0x34, 0x44};
uint8_t broadcastAddress2[] = {0x84, 0xF3, 0xEB, 0xCA, 0xF8, 0xD3};
ESP Now DHT11 Sensor Code
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "DHT.h"
DHT dht;
uint8_t broadcastAddress1[] = {0x30, 0xC6, 0xF7, 0x23, 0x34, 0x44};
uint8_t broadcastAddress2[] = {0x84, 0xF3, 0xEB, 0xCA, 0xF8, 0xD3};
String success;
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;
struct_message DHT11_data;
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
char macStr[18];
Serial.print("Delivery Status of: ");
snprintf(macStr, sizeof(macStr), "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
Serial.print(macStr);
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? " Send Successfully" : " Fail to send");
if (status ==0){
success = "Delivery Success :)";
}
else{
success = "Delivery Fail :(";
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
dht.setup(0); /*Connect the DHT11's data pin to GPIO0*/
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
peerInfo.channel = 0;
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress1, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK){
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress2, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK){
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
}
void loop() {
DHT11_data.temp = dht.getTemperature(); /*Get the Temperature value*/
DHT11_data.hum = dht.getHumidity(); /*Get the Humidity value*/
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(0, (uint8_t *) &DHT11_data, sizeof(struct_message));
if (result == ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Sent Successfullt");
}
else {
Serial.println("Getiing Error while sending the data");
}
delay(3000);
}
- Now upload the code on sender ESP32. (While uploading the code make sure your ESP32 board is in the boot mode.)
- After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200 then reset the ESP32 board and check the output as shown in the below image
.png)
Understand the code
Add esp_now.h, DHT.h, and WiFi.h libraries.
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include "DHT.h"Create the object as below
DHT dht;Now add the MAC address of receiver ESP32
Our MAC address is 30:C6:F7:23:34:44
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0x30, 0xC6, 0xF7, 0x23, 0x34, 0x44};Here we have created a structure to send the data.
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;Create a struct_message variable called DHT11_data.
struct_message DHT11_data;esp_now_peer_info_t is a variable to store information of peers.
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;OnDataSent() is a callback function that will be executed when a message is sent.
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
char macStr[18];
Serial.print("Delivery Status of: ");
snprintf(macStr, sizeof(macStr), "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
Serial.print(macStr);
Serial.println(status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS ? " Send Successfully" : " Fail to send");
if (status ==0){
success = "Delivery Success :)";
}
else{
success = "Delivery Fail :(";
}
}
In the setup function,
initialize the serial monitor
Serial.begin(115200);set the GPIO 0 pin as a data communication Pin.
dht.setup(0);Set ESP32 is a Wi-Fi station Mode:
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);Initialize ESP-NOW:
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}Now, register the callback function that will be called when a message is sent.
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);After that, we need to pair with first ESP device to send data. That’s what we do in the next lines:
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress1, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK){
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}Similarly, pair with a second nodemcu device.
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress2, 6);
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK){
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
In the loop function
Get the temperature and humidity reading from DHT11 and store it.
DHT11_data.temp = dht.getTemperature(); /*Get the Temperature value*/
DHT11_data.hum = dht.getHumidity(); /*Get the Humidity value*/Here we’ll send the temperature and humidity every three second.
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(0, (uint8_t *) &msg,sizeof(msg));Check the message status was successfully sent or not
if (result == ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Sent with success");
}
else {
Serial.println("Error sending the data");
}Wait for three second
delay(3000);Now copy the below code and upload it on the second device and check the result on the serial monitor.
Before uploading make sure you have updated your MAC address
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0xXX, 0xXX, 0xXX, 0xXX, 0xXX, 0xXX };
ESP Now ESP32 Slave Receiver-1 Code
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
float DHT11_Temp;
float DHT11_Hum;
String success;
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;
struct_message DHT11_data;
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t * mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&DHT11_data, incomingData, sizeof(DHT11_data));
DHT11_Temp = DHT11_data.temp;
DHT11_Hum = DHT11_data.temp;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.temp);
Serial.println(" ºC");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.hum);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.println();
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop() {}
- Now upload the code on ESP32 Receiver. (While uploading the code make sure your ESP32 board is in the boot mode.)
- After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200 then reset the ESP32 board and check the output as shown in the below image
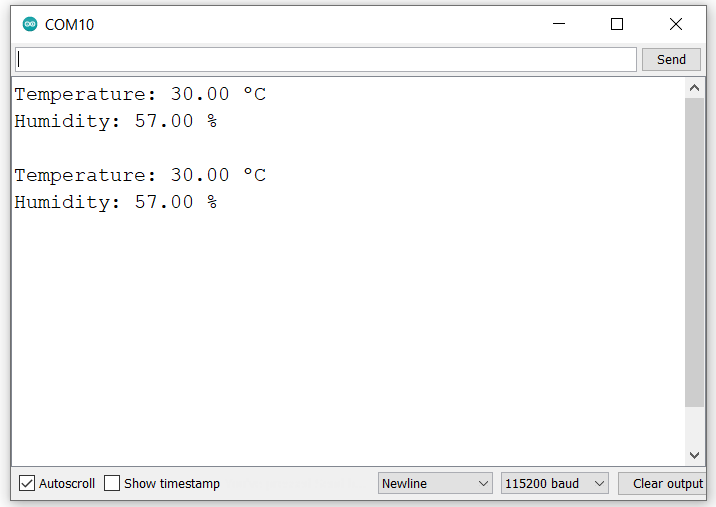
Understand the code
Add esp_now.h and WiFi.h libraries.
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>Here we are created a structure to send and receive the data.
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;Create a struct_message variable called DHT11_data and BMP180_data.
struct_message DHT11_data;esp_now_peer_info_t is a variable to store information of peers.
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;Create a callback function that will be called when the ESP32 receives the data via ESP-NOW.
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t * mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&DHT11_data, incomingData, sizeof(DHT11_data));
DHT11_Temp = DHT11_data.temp;
DHT11_Hum = DHT11_data.hum;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.temp);
Serial.println(" ºC");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.hum);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.println();
}In the setup function,
initialize the serial monitor
Serial.begin(115200);Set ESP32 is a Wi-Fi station Mode:
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);Initialize ESP-NOW:
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}Now, register the callback function that will be called when a message is sent.
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
As receiver-1, we can upload the similar code to receiver-2 and check the received data, it will be the same.
ESPNOW NodeMCU Slave Receiver-2 Code
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <espnow.h>
float DHT11_Temp;
float DHT11_Hum;
String success;
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;
struct_message DHT11_data;
void OnDataRecv(uint8_t * mac, uint8_t *incomingData, uint8_t len) {
memcpy(&DHT11_data, incomingData, sizeof(DHT11_data));
DHT11_Temp = DHT11_data.temp;
DHT11_Hum = DHT11_data.hum;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.temp);
Serial.println(" ºC");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.hum);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.println();
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
if (esp_now_init() != 0) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_set_self_role(ESP_NOW_ROLE_SLAVE);
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop() {}
- Now upload the code on NodeMCU Receiver.
- After uploading the code open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 115200 then reset the NodeMCU board and check the output as shown in the below image
.png)
Understand the code
Add esp8266WiFI.h and espnow.h libraries.
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <espnow.h>Here we are created a structure to send and receive the data.
typedef struct struct_message {
float temp;
float hum;
} struct_message;Create a struct_message variable called DHT11_data and BMP180_data.
struct_message DHT11_data;Create a callback function that will be called when the ESP32 receives the data via ESP-NOW.
void OnDataRecv(uint8_t * mac, uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&DHT11_data, incomingData, sizeof(DHT11_data));
DHT11_Temp = DHT11_data.temp;
DHT11_Hum = DHT11_data.temp;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.temp);
Serial.println(" ºC");
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(DHT11_data.hum);
Serial.println(" %");
Serial.println();
}
In the setup function,
initialize the serial monitor
Serial.begin(115200);Set ESP32 is a Wi-Fi station Mode:
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);Initialize ESP-NOW:
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}Now, register the callback function that will be called when a message is received.
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
Components Used |
||
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 WROOM WiFi Development Tools - 802.11 ESP32 General Development Kit, embeds ESP32-WROOM-32E, 4MB flash. |
X 3 | |