Introduction
On-line vehicle tracking system track the location and speed of vehicle. It shows the real-time location and speed of vehicle on Dashboard created on Adafruit IO. For tracking location and speed GPS receiver is used. This tracking data send to the cloud using wi-fi module ESP8266.
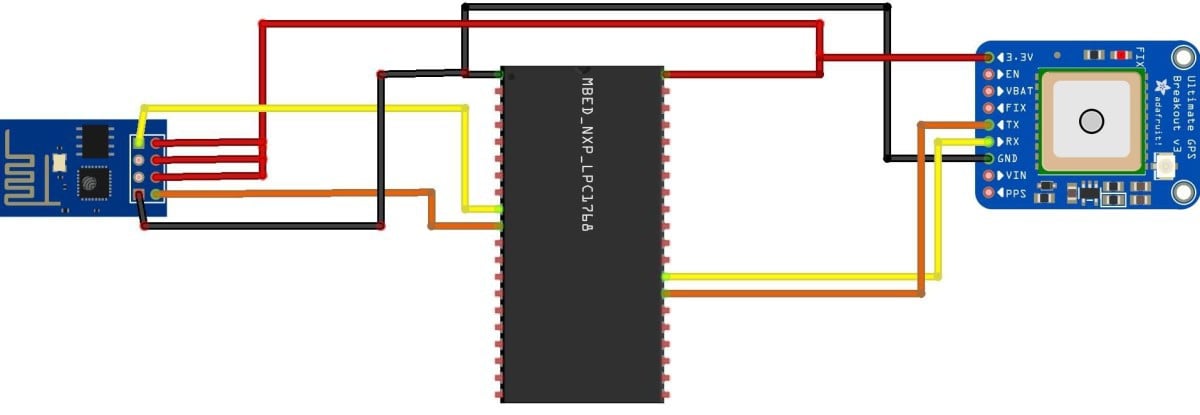
Circuit Diagram
Project Working
- GPS module read the frame from satellites continuously. By reading this GPS information serially using MBED controller and extracted the required information like Latitude, Longitude, Speed, Altitude.
- Latitude, Longitude, Speed, Altitude these parameters are calculated from valid frame(GPRMC, GPGGA NMEA string).
- These tracking parameter along with vehicle speed are uploaded to Adafruit IO's Dashboard. On Adafruit Dashboard, we can see on-line vehicle tracking.
Latitude & Longitude Extraction
if(sscanf(msg, "GPRMC,%f,%c,%f,%c,%f,%c,%f,%d", &time,&m, &latitude, &ns, &longitude, &ew,&speed, &lock) >= 1) {
{
if(!lock) {
longitude = 0.0;
latitude = 0.0;
return 0;
} else {
sscanf(msg,"GPGGA,%f,%f,%c,%f,%c,%d,%d,%*f,%d", &time, &latitude1, &ns, &longitude1, &ew, &fq, &nst, &tst, &altitude);
if(ns == 'S') { latitude *= -1.0; }
if(ew == 'W') { longitude *= -1.0; }
float degrees = trunc(latitude / 100.0f);
float minutes = latitude - (degrees * 100.0f);
latitude = degrees + minutes / 60.0f;
degrees = trunc(longitude / 100.0f); //* 0.01f);
minutes = longitude - (degrees * 100.0f);
longitude = degrees + minutes / 60.0f; - In above code latitude and longitude converted in to degree and minutes and then using this degree and minutes latitude and longitude are calculated.
Speed Calculation
- Speed given by GPS is in knots to convert it into kmph multiply it by 1.85.
float a=gps.spd*1.85; //converting speed in to kmphConnect to Internet
- System is connected to internet using ESP8266 wifi-module.
NetworkInterface* network = easy_connect(true);
if (!network) {
return -1;
}Adafruit IO
- System is connected to io.adafruit.com
const char* hostname = "io.adafruit.com";
int port = 1883;
logMessage("Connecting to %s:%d\r\n", hostname, port);
int rc = mqttNetwork.connect(hostname, port);
if (rc != 0)
logMessage("rc from TCP connect is %d\r\n", rc);- Create Dashboard and create feeds on io.adafruit.com.
- Mention feed path, username, AIO key to connect system to your dashboard.
data.clientID.cstring = "username/feed/name/csv";
data.username.cstring = "username";
data.password.cstring = "AIO key";
if ((rc = client.connect(data)) != 0)
logMessage("rc from MQTT connect is %d\r\n", rc);- This data is published to adafruit using MQTT protocol.
//publishing latitude, longitude and altitude
char buf[200];
sprintf(buf, "%f,%f,%f,%d",a,b,c,d);
message.qos = MQTT::QOS0;
message.retained = false;
message.dup = false;
message.payload = (void*)buf;
message.payloadlen = strlen(buf)+1;
rc = client.publish(topic, message);
output.printf("rc=%d",rc);
//Publishing speed
sprintf(buf,"%f",a);
message.qos = MQTT::QOS0;
message.retained = false;
message.dup = false;
message.payload = (void*)buf;
message.payloadlen = strlen(buf)+1;
rc = client.publish(topic1, message);
output.printf("rc=%d",rc);
Adafruit Dashboard
Video