Digikey list url : https://www.digikey.in/en/mylists/list/CYXHH434IO
SWAT ( Sattelite based Water Analysis and Tracking)
Motive:
A clear gap existed between available tracking technologies and their practical implementation in public-utility sectors. To address this, the SWAT initiative was developed as an autonomous tanker-tracking and monitoring system. The goal is to enable transparent, real-time oversight of water tankers, especially in regions facing droughts or severe water scarcity where proper allocation and monitoring are essential.
1. Hardware Selection
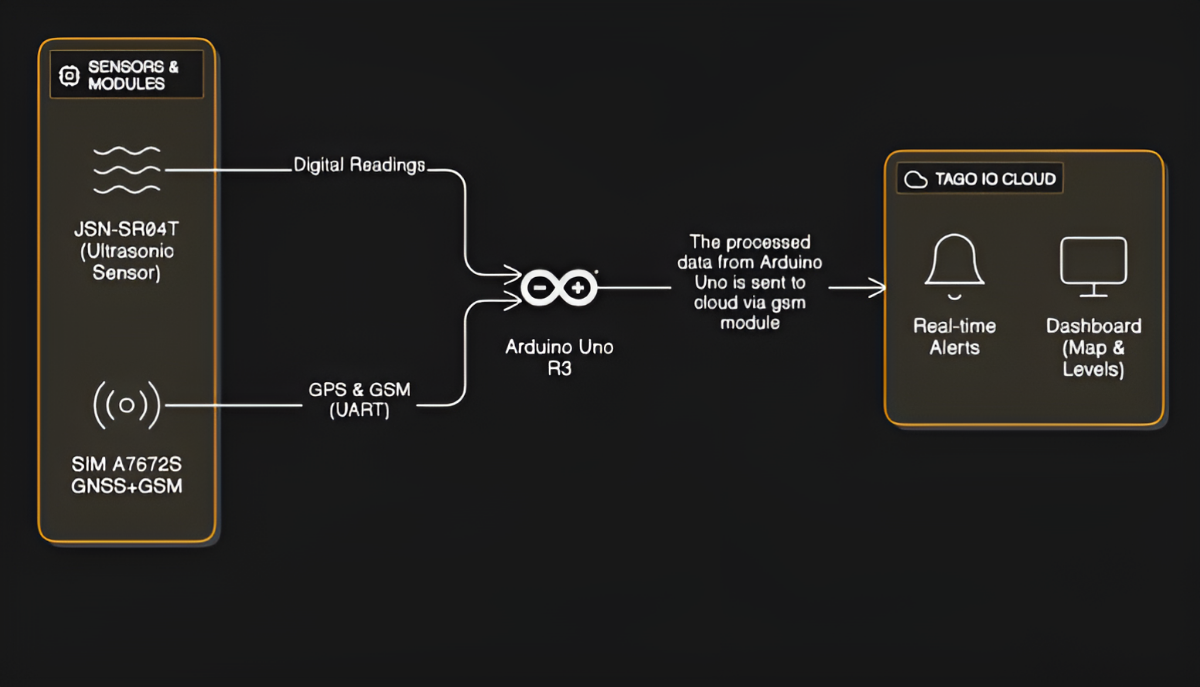
The system required stable mobile connectivity, so LTE communication was the foundation. An LTE + GNSS module was selected, providing:
- Continuous GNSS data (location, speed, heading, timestamp)
- Reliable LTE transmission of processed telemetry
To simulate water-level monitoring at prototype scale, a waterproof ultrasonic sensor was chosen due to its accuracy and resilience in outdoor applications.
2. System Architecture & Circuit Design
A full architecture was designed after aligning component communication protocols, voltage requirements, and data flow. The schematic outlined:
- Power distribution
- Sensor integration
- GNSS/LTE communication flow
- Microcontroller logic
- Cloud communication endpoints
This provided a clear blueprint for building and debugging the system.
3. Hardware Assembly & Validation
The circuit was assembled according to the schematic. Each component’s readings and communications were verified using a serial monitor to ensure clean data acquisition before cloud integration.
Demo Video:
https://youtube.com/shorts/ta-VV7v__Tw
4. Cloud Integration
Data was transmitted to the cloud using HiveMQ MQTT broker.
A Node.js-based dashboard was built with OpenStreetMap API to display real-time tanker movement, sensor readings, and status.
This setup offered a lightweight, scalable, and fully browser-accessible interface.
.jpg)
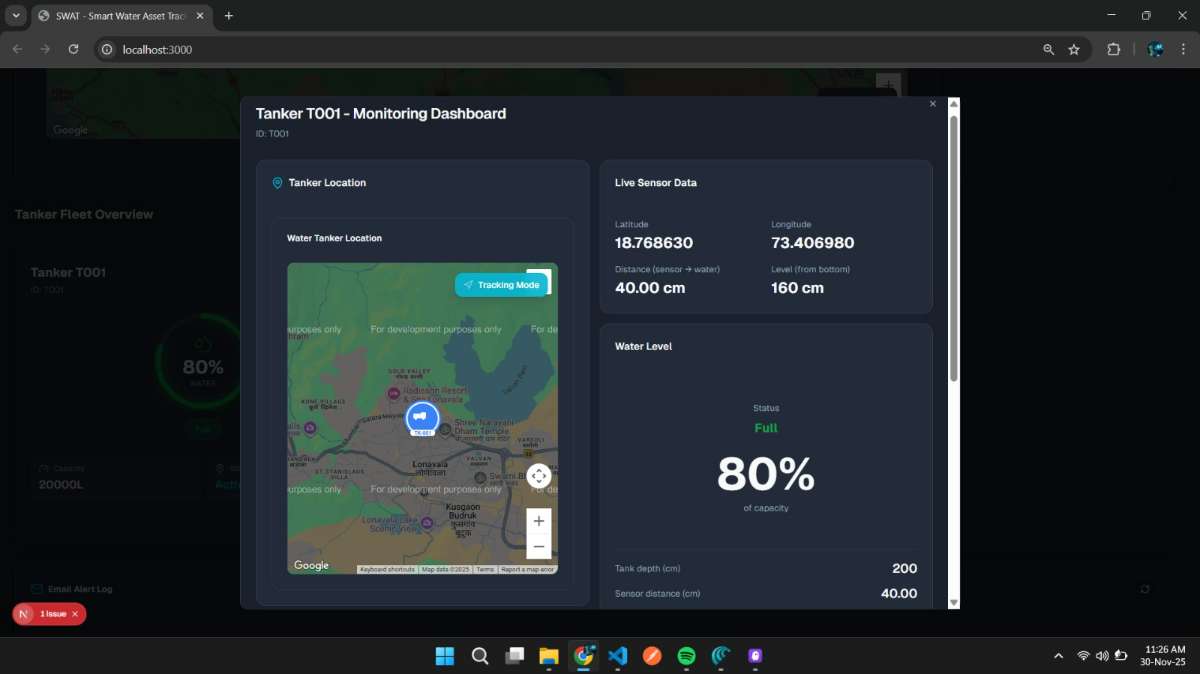
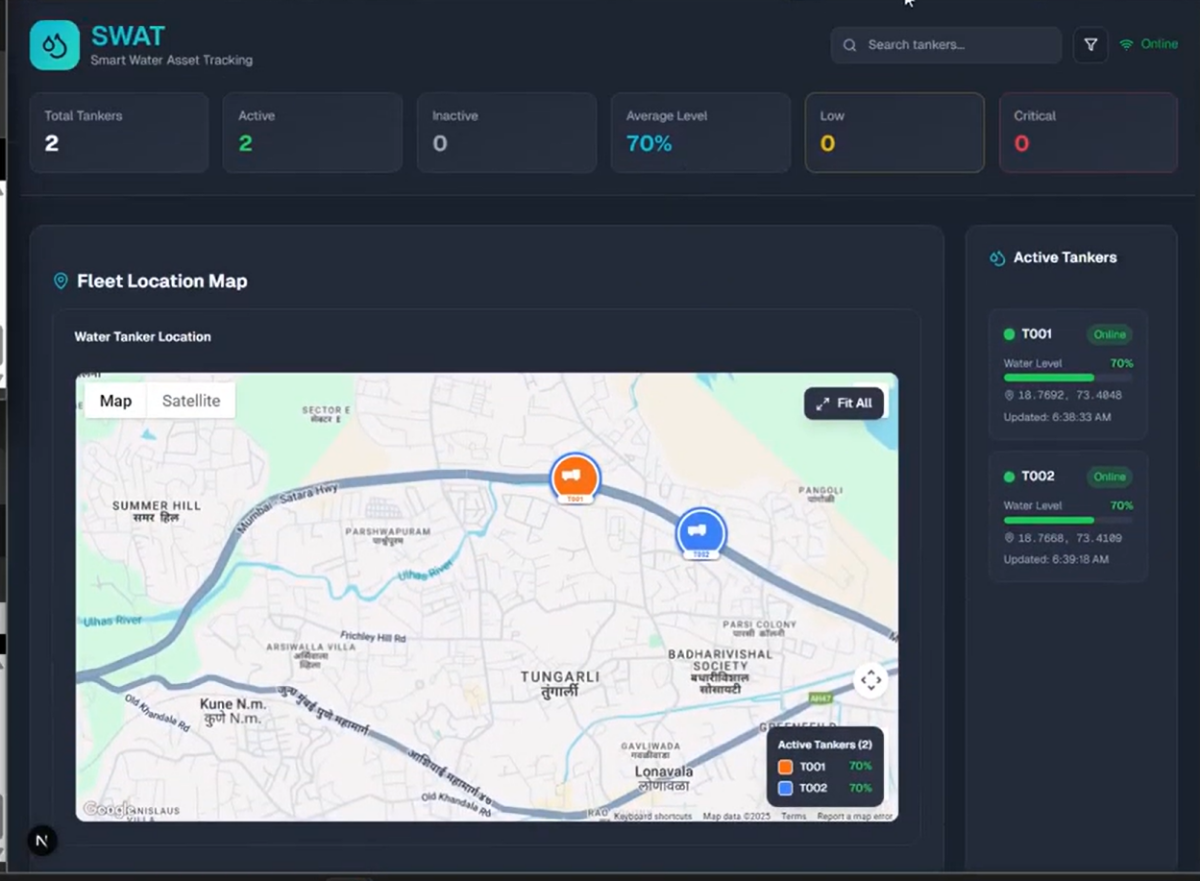
5. Real-World Testing
Two primary operational scenarios were validated:
a) Multi-Device Load Behavior
Using Wokwi simulations, multiple virtual tankers were created to test how the dashboard handled parallel data streams. The system synchronized and displayed each device without inconsistency.
Youtube Link:
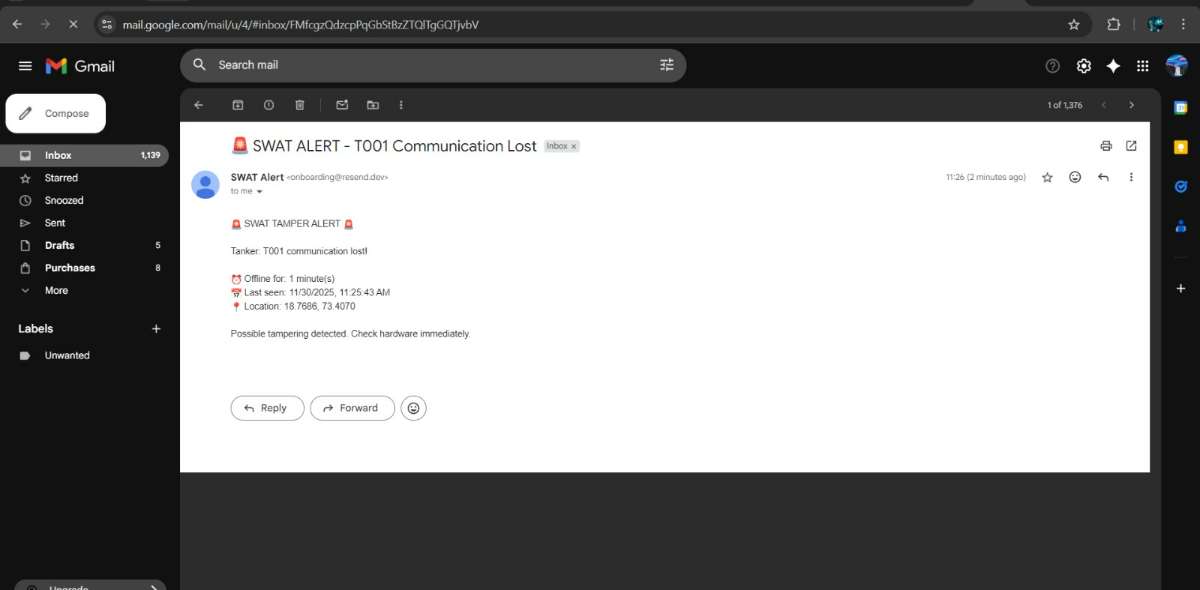
b) Tamper Simulation
Powering off the device simulated unauthorized shutdown. The system identified the anomaly and triggered email notifications for the tamper event.
6. AI-Driven Enhancements
To expand the system beyond basic tracking, AI components were integrated using free, open-source models that are actually deployable, not theoretical fluff.
a) Intelligent Route Optimization
Model Used:
- Google OR-Tools Routing Solver
How it works:
- Historical routes + timestamps are logged.
- Traffic data from OSM or free traffic APIs is merged.
- OR-Tools solves optimal paths using Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) logic.
Tech Stack:
- Python microservice running OR-Tools
- Node.js frontend consuming optimized route results
- MongoDB or PostGIS for storing geospatial and historical datasets
Outcome:
Real-time route optimization and dynamic rerouting during high-demand periods.
b) AI-Based Autonomous Tamper Detection
Models Used:
- Isolation Forest
- One-Class SVM
(both free in scikit-learn, lightweight, and reliable for anomaly detection)
Training Features:
- GNSS stability & drift
- Water-level change velocity
- Power/voltage irregularities
- MQTT packet drop patterns
- Speed anomalies
- Route deviation scores
Pipeline:
- Train the model on 1–2 weeks of stable “normal” behavior
- Run inference continuously on incoming live data
- Flag deviations automatically
- Trigger Node.js email alerts on high anomaly scores
Outcome:
Accurate tamper detection beyond simple power-loss events.