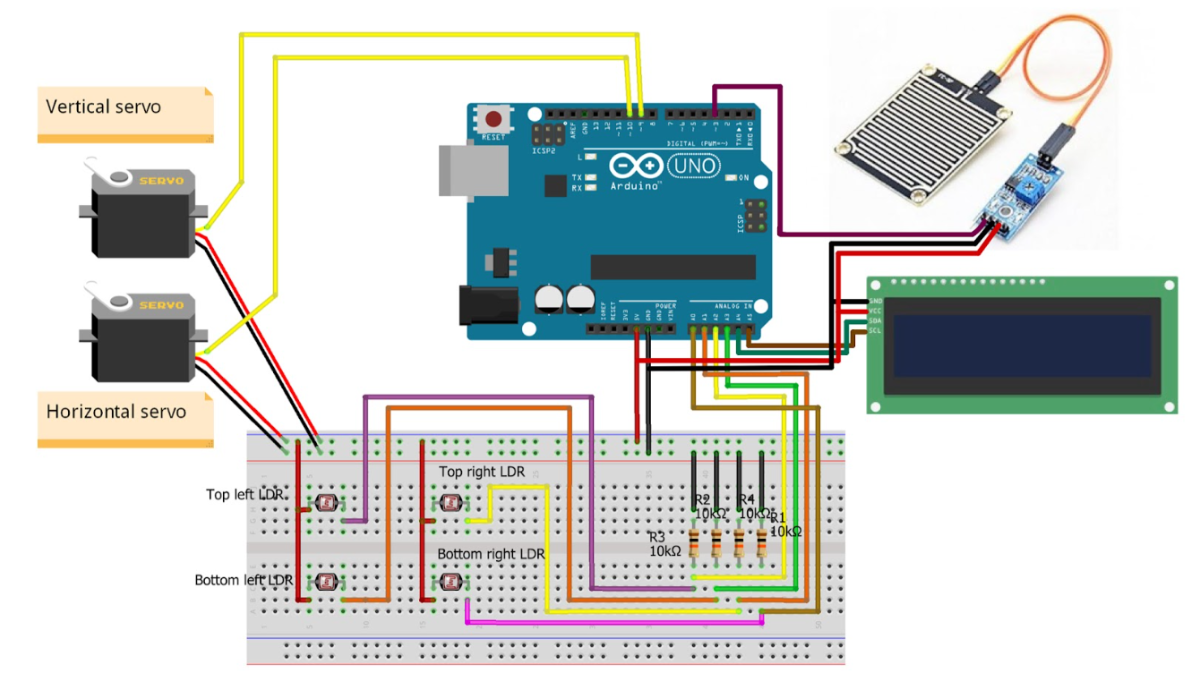
Step 1: Hardware Assembly
Steps:
- Mount the Solar Panel on a servo-driven dual-axis frame.
- Attach 4 LDRs on each corner of the panel to detect sunlight intensity.
- Connect Servo Motors to Arduino PWM pins for axis control.
- Interface Rain Sensor Module to Arduino digital input pins.
- Connect Raspberry Pi Camera (or USB webcam) to Raspberry Pi.
NodeMCU Setup for sending sensor data to ThingSpeak/Azure IoT
Step 2: Arduino Programming (Sun & Rain Control)
- Write code to:
- Continuously read LDR values and adjust servo motors to align with the highest light intensity.
- Monitor Rain Sensor to override tracking and tilt panel to a safe position.
- Upload code using Arduino IDE.
- Step 3: Raspberry Pi Edge AI with OpenCV
- Install Python, OpenCV on Raspberry Pi.
- Write a Python script to:
- Capture images or video streams.
- Detect cloud density or shading using image processing.
- Adjust panel alignment for maximum efficiency.
- Integrate ML model (optional) to predict weather patterns.
- Example of AI-based Cloud Detection:
- Step 4: IoT Cloud Integration
- NodeMCU ESP8266 is used to upload sensor data to:
- ThingSpeak for live data visualization.
- Azure IoT Hub for analytics and dashboarding.
- Use MQTT/HTTP protocol to send data.
- Step 5: Testing & Demo Video
- Test sun tracking by using a torch to simulate sunlight.
- Spray water on the rain sensor to simulate rain response.
- Observe panel adjusting automatically.
Monitor data logging on ThingSpeak/Azure dashboard.
Working Video:
Circuit Diagram: