GROUND HYDROGENOUS MANAGING PROBE
The moisture of the soil plays an essential role in the irrigation. As nutrients in the soil provide the food to the plants for their growth, Supplying water to the plants is also essential to change the temperature of the plants and it must be in efficient amount. soil moisture levels can guide to anaerobic situations that can encourage the plant’s growth as well as soil pathogens, which are the enhancer of the plant yield.
We are here to give a better solution for poor moisture in our field, that is a major drawback of our agricultural system. We can detect the moisture level of the ground and can irrigate it with perfect level of water. This increase the agriculture rank and make it to reach the next level in yield.
Components used:
1. Breadboard
2. Audrino - UNO
3. Submersible pool water pump-240L/H
4. Wall adapter power supply - 12VDC 2A
5. Soil moisture sensor
6. HC-05 Bluetooth serial module
7. N-channel MOSFET 60V-30A
8. 10 K ohm resistor
9. Water flow sensor - G1/2"
10. Female DC power adapter 2.1mm jack to screw terminal block
11. USB cable A-B
12. Jumper wires pack M/M
13. Male header pack-Break-Away
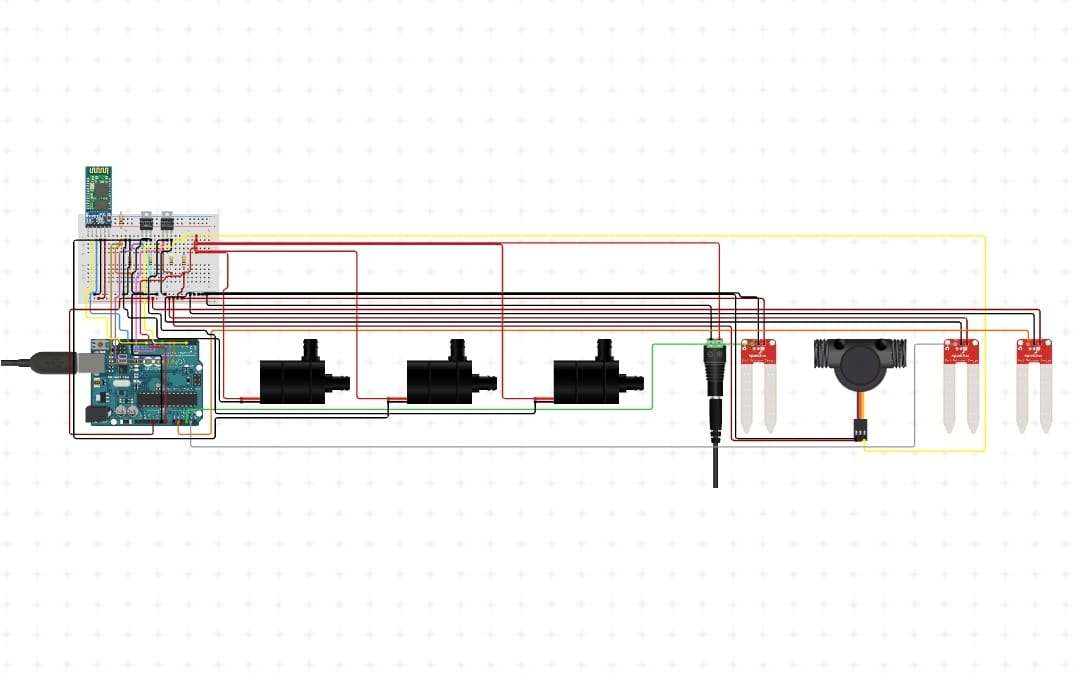
In this project, we are going to build a transistor base soil moisture detector circuit and auto water irrigator.
A breadboard is connected preferably to an analog device, here we say Audrino UNO.
As Audrino is a microcontroller, it takes charge over this process, as we designed it to suit our preferring output. The module produces an output voltage according to the resistance of the probe and is made available at an Analog Output (AO) pin
Moisture sensor is connected to it,The fork-shaped probe with two exposed conductors, acts as a variable resistor,This resistance is inversely proportional to the soil moisture:
The more water in the soil means better conductivity and will result in a lower resistance.
The less water in the soil means poor conductivity and will result in a higher resistance.
The sensor produces an output voltage according to the resistance, which by measuring we can determine the moisture level, as it measures the volumetric water content in the soil which is the core to be known here.
Then we connect a N-channel MOSFET of 60V, as the output from the sensor is much less, it can't be enough to pump the water, where water pump requires 12-20V. So a transistor is connected, here MOSFET.
Once the sensor reading is calculated by our sensor, our pump ready to work. when the moisture level in the soil crosses a threshold, you can activate a relay to start pump.
A Bluetooth module is also connected to check the status of the water instantly, which is an additional beneficial option.
WIRING :
Let’s hook the soil moisture sensor up to the Arduino.
First you need to supply power to the sensor. For that you may connect the VCC pin on the module to 5V on the Arduino.
However, one commonly known issue with these sensors is their short lifespan when exposed to a moist environment. Having power applied to the probe constantly speeds the rate of corrosion significantly.
To overcome this, we recommend that you do not power the sensor constantly, but power it only when you take the readings.
An easy way to accomplish this is to connect the VCC pin to a digital pin of an Arduino and set it to HIGH or LOW as per your requirement.
Also the total power drawn by the module (with both LEDs lit) is about 8 mA, so it is okay to power the module off a digital pin on an Arduino.
So, let’s connect the VCC pin on the module to the digital pin #7 of an Arduino and GND pin to ground.
Finally, connect the AO pin on the module to the A0 ADC pin on your Arduino.
VCC supply is then given to the pump, so that it can pump water to the field as per the requirement.
And finally from Bluetooth module we can get the data about the irrigation level and water content of the ground instantly.
Finally, it's an efficient device that can bring agriculture to the best level up.
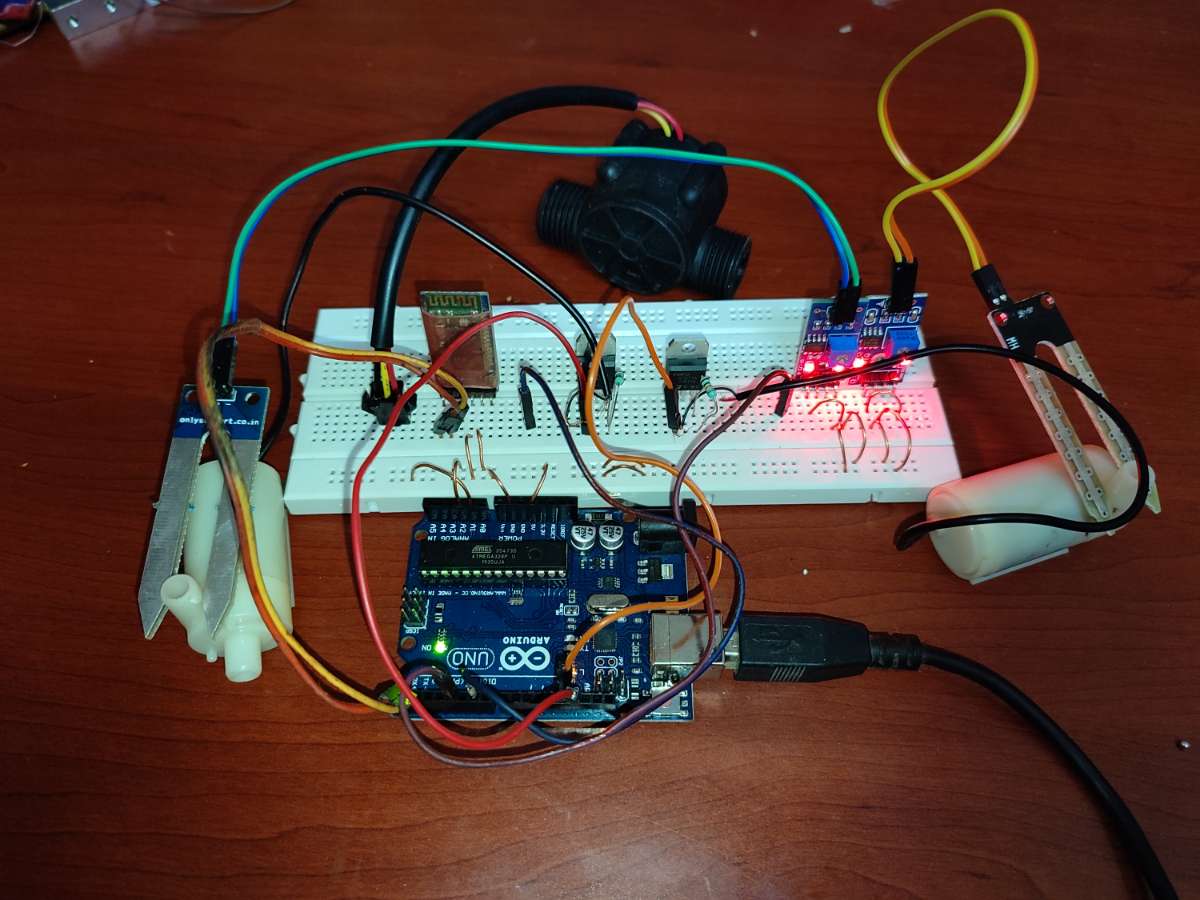
FINAL BUILT:
Based on the calibration values, the program below defines the following ranges to determine the status of the soil:
< 500 is too WET- (500-750 is the target range)
> 750 is dry enough to be watered.
It can be monitored by the Bluetooth device, which is most efficient way from we can know the up to date information of our field.
This is the device, we have desinged that going to be a gamechanger in the field of agriculture.