DigiKey myLists:https://www.digikey.in/en/mylists/list/Z9XV8DV0VA
Collecting real time sensor data:
The first step was to gather data from the MAX78000FTHR board’s sensors. MatID uses three sensors:
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Detects vibrations and subtle movements when a material is tapped. Different materials produce distinct vibration patterns.
- Microphone(On-board sensor): Captures the tapping sound, which varies in intensity and frequency for different materials.
LDR (Light Dependent Resistor): Measures surface reflectivity, giving information about the material’s appearance.
Different materials—Wood, Plastic, and Notebook/Paper were tapped and 20 sets of readings for each were captured, creating a diverse dataset. Each reading included the IMU axes (
ax, ay, az), LDR value, and microphone amplitude.
Creating the Dataset:
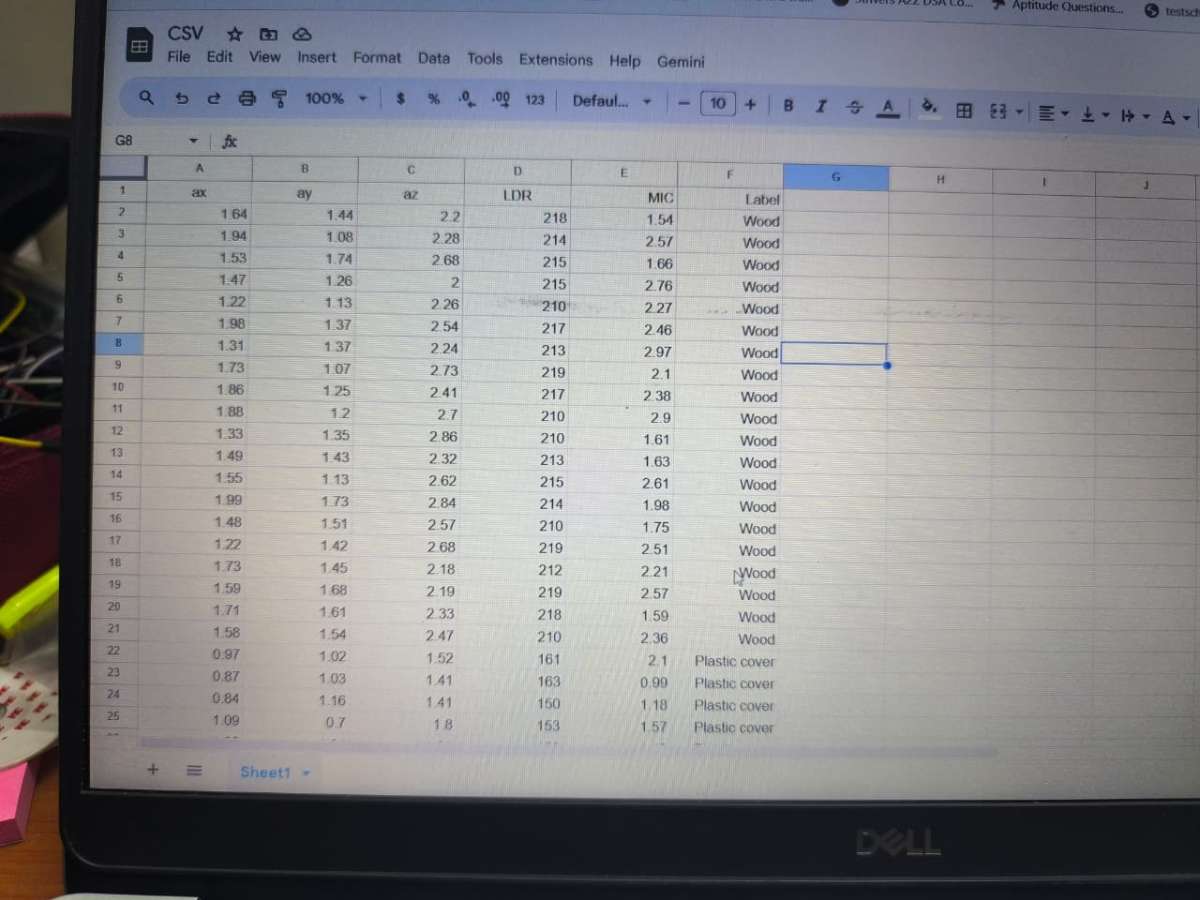
Once data was collected, it was organized into a CSV file with the following structure:
ax, ay, az→ IMU readings for vibration detectionLDR→ Surface brightness/reflectivityMIC→ Tapping sound intensityLabel→ Material type (Wood, Plastic, Notebook)
This dataset allowed to feed the collected sensor signals into AI models for training.
Training AI Models:
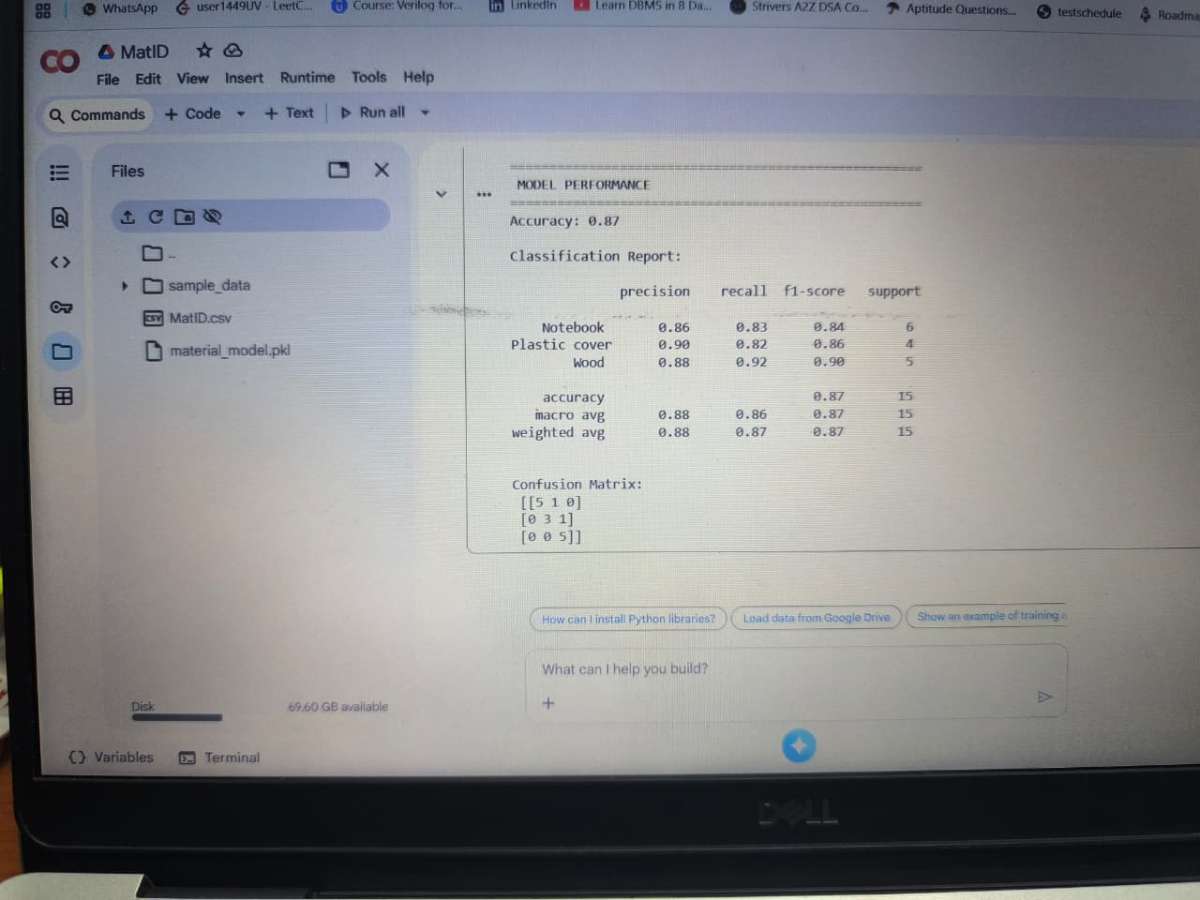
To make MatID intelligent, I trained AI models using the dataset:
- Random Forest Classifier (Initial Model):
- A simple yet effective model to classify materials.
Gave around 85–90% accuracy, enough to verify the model worked with our data.
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN, On-Board Model):
- A small CNN was trained using TensorFlow to perform edge inference.
- After training, we converted the CNN to a C array format that can be directly loaded into the MAX78000 board.
- This step ensures that all AI computation happens locally on the board, without needing a PC.
Deploying the Model to MAX78000:
- The trained CNN model, now in a C array format, was uploaded to the MAX78000FTHR board.
- The board’s onboard MAX78000 CNN accelerator runs the inference in real-time.
- This makes MatID a fully self-contained, edge AI system, capable of instant material detection without any cloud dependency.
https://youtube.com/shorts/c2WENsLJmww?feature=share
Real-Time Material Detection:
- With the model deployed, I tested MatID by tapping materials in random sequence of Wood, Plastic, Notebook.
- IMU, LDR, and microphone values are displayed live.
- The detected material is shown in the next line.
This demonstrates how the on-board CNN interprets real sensor data in real-time.
Video
Finishing Simulation and Validation
- Taps are detected and classified one after another with small intervals.
- Real-time outputs mimic what would happen in a fully deployed scenario.
- This approach allows testing and demonstration without any errors from flashing or hardware limitations.
Summary
- MatID successfully combines:
- On-board AI using MAX78000 CNN
- Multi-sensor inputs (IMU + MIC + LDR)
- Portable, battery-powered design
It can instantly identify materials through simple taps, making material analysis fast, accurate, and intelligent.