Azure IoT Hub, the cloud computing service by Microsoft enables developers to connect, monitor, and manage billions of IoT devices on a single platform. It is already used in various IoT applications like home automation systems, security, surveillance, and monitoring systems. To demonstrate the capabilities of Azure IoT hub, we are going to build a small circuit with the Raspberry Pi, a DHT11 Temperature, and Humidity Sensor, in order to process the sensor data with it. Finally, we will publish sensor data to the Azure IoT server using the MQTT protocol. In this tutorial, we will learn how to set up and configure an Azure server and send data using a Raspberry Pi.
Creating an Azure IoT Hub
We are ready to do all the necessary setups that are required for setting up Microsoft Azure services but before that, make sure you have a Microsoft account. If you do not have that, you can simply sign up. Thereafter, go to the Azure portal using portal.azure.com and log in.
Once you are logged in, go to the Azure homepage, select the Create a resource button, and then search for IoT Hub in the Search the Marketplace field. Select IoT Hub from the search results, and then select Create. The images below will give you a better idea of the process.
Fill in Necessary Details to Create an IoT Hub.
In the Subscription section, you need to select the subscription to use it for your hub. In our case, we are opting for a Trial account and we have selected “Free Trial”.
Next, in the Resource Group Section, select your resource group. If you do not have one, you need to create a new one by clicking on the Create new and enter the name of the Resource.
In the Region Section, you can use the dropdown menu to select your preferred region.
In the IoT Hub Name Section, you need to enter a name for your hub. This must be unique. All the necessary communications will happen with this name.
Under Tab “Size and Scale”, select “Free Tier” and Click on Next. Then click on “Review+Create”. It will take a few minutes to create the IoT Hub. Click on the name of the IoT Hub you created. Note down the Hostname from the window as shown in the image below. Then click on the Shared access policies in the Settings. Shared access policies are highlighted in the image below. Click on the iothubowner option under Policy. Note down the Primary key and Connection string-primary key for future references. Now, to Register a New Device under IoT Hub, Click on IoT Devices. In the Device Explorer pane, click on Add to add a device to the hub.
Fill in the Following Information in the New Devices Tab.
- Device ID: Enter Id for the device. Device Ids need to be unique.
- Authentication Type: Select a Symmetric Key.
- Auto Generate Keys: Select this check box.
- Connect Device to IoT Hub: Click Enable.
Once the device is created, you can find your newly created device on the Device Explorer section. Click on the name of the device. It will show the details of the device. Note down the Primary key and the Connection string-primary key of the Device. This is important as we need it for communication.
Now, when that is done, we can move on to the hardware side of things.
Components Required to Build our Test Circuit for Azure IoT with Raspberry Pi
As the hardware portion of this circuit is very simple, the component requirement too is very simple. A list of required components is shown below.
- Raspberry Pi 3B (We can also use any other models of Pi)
- Micro SD Card-16 GB
- DHT11 Sensor
- Micro USB 5V, 2.4A Power supply
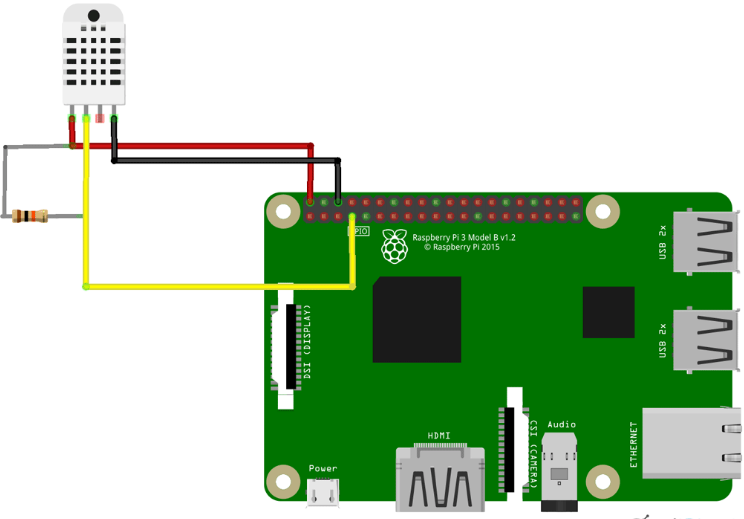
The above circuit sends Temperature and Humidity data to Microsoft IoT Hub. In this circuit, we have used a DHT11 sensor to collect the Temperature and Humidity data and we are using a Raspberry Pi 3B as a data processing device. The DHT11 sensor has three pins. The VCC and GND pins are used to give 5V DC supply to the sensor and the Data output pin of DHT11 is connected to GPIO4 of Raspberry Pi.
Programming Raspberry Pi to Publish Data on Azure IoT Hub
Before starting the coding for this project, we need to create an Azure cloud shell (CLI) in the Azure portal. This will come in handy in many ways. For that, click on the Azure cloud shell button in the portal.
Once done, you can open the CLI, and run the following commands to install the Azure add-on’s which will be used to show the sensor data.
az extension add --name azure-cli-iot-ext
Once that’s done, we need to install dependencies on the Raspberry Pi to communicate with the DHT11 sensor and to make the communication process easy for Azure IoT services. For that open up a Raspberry Pi Terminal to install the dependent packages used in the project.
First, we need to download the DHT library for Raspberry Pi, then extract it from the root folder and run the following command to install it.
sudo python setup.py installAfter successful installation, run the following commands to install all the dependent packages on Azure IoT Hub.
sudo pip3 install azure-iot-device
sudo pip3 install azure-iot-hub
sudo pip3 install azure-iothub-service-client
sudo pip3 install azure-iothub-device-client
Once we have completed installing all the prerequisites, it’s time to write the code in Python.
import random
import Adafruit_DHT
import time
from azure.iot.device import IoTHubDeviceClient, Message
sensor = Adafruit_DHT.DHT11
pin = 4
CONNECTION_STRING = "HostName=xxxxxxxx;DeviceId=xxxxxx;SharedAccessKey=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
MSG_SND = '{{"temperature": {temperature},"humidity": {humidity}}}'
while True:
humidity, temperature = Adafruit_DHT.read_retry(sensor, pin)
def iothub_client_init():
client = IoTHubDeviceClient.create_from_connection_string(CONNECTION_STRING)
return client
def iothub_client_telemetry_sample_run():
try:
client = iothub_client_init()
print ( "Sending data to IoT Hub, press Ctrl-C to exit" )
while True:
msg_txt_formatted = MSG_SND.format(temperature=temperature, humidity=humidity)
message = Message(msg_txt_formatted)
print( "Sending message: {}".format(message) )
client.send_message(message)
print ( "Message successfully sent" )
time.sleep(3)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print ( "IoTHubClient stopped" )
if __name__ == '__main__':
print ( "Press Ctrl-C to exit" )
iothub_client_telemetry_sample_run()
Python code is given here, we will change the value of CONNECTION_STRING with the device-primary connection string that we saved earlier.
We will upload the code in the raspberry pi.
Publish Data on Azure IoT Hub – Testing
After successfully writing the code, compile it and check for any errors. If the code block is compiled successfully, then run the code. In the Terminal window, you should see the message saying, "Message successfully sent".
Now, to see the data in Azure IoT Hub, go to the portal and click on the CLI Terminal and run the following commands replacing your credentials in it.
az iot hub monitor-events --hub-name XYZ --device-id XYZ
Note:
Replace XYZ with your Hub name and Device id.
After running the above command, you should get the data.
