SmartDash is a real-time driver monitoring system powered by the MAX78000 Edge-AI MCU.
It detects drowsiness, eye closure, yawning, and distraction directly on the device — no cloud, no external GPU, no latency.
An ESP8266 module connects the system to Firebase, enabling remote monitoring of fatigue events on a live dashboard:
👉 Dashboard: https://dhirendrag.github.io/vehicle-dashboard/
Because all inference runs locally, SmartDash ensures:
- Zero privacy concerns
- Ultra-fast response
- Low power consumption
- No bandwidth usage except for alerts
Introduction
Driver drowsiness and distracted driving are major contributors to road accidents worldwide. While commercial driver-monitoring systems exist, they are often expensive, require cloud processing, and compromise user privacy.
SmartDash addresses this critical social problem by using Edge AI running entirely on the MAX78000 microcontroller to detect eye closure, drowsiness, yawning, and distraction in real time. By combining low-power hardware, on-device AI inference, and dashcam integration, SmartDash offers a creative, modern, and cost-effective approach to an existing challenge.
The system influences driver behavior by:
- Encouraging safer driving habits
- Making drivers more aware of fatigue
- Delivering instant feedback that helps prevent accidents
- Enabling fleet managers to view fatigue data for improved safety oversight
By eliminating dependence on cloud AI—which is expensive, slow, and bandwidth-heavy—SmartDash provides an instant-response, privacy-preserving safety companion suitable for all vehicle types, from personal cars to commercial fleets.
System Overview
Main Components
- MAX78000FTHR – Edge AI microcontroller for running the CNN
- HM01B0 Camera – Ultra-low-power camera for eye tracking
- ESP8266 – WiFi module for uploading alert data to Firebase
- MPU6050 – IMU for head-movement and distraction detection
- TEMT6000 – Ambient light sensor for low-light compensation
- GPS Module (NEO-M9N) – Vehicle location logging
- Buzzer + NPN transistor – Driver alert mechanism
- Li-ion power system
Hardware Setup
Wiring Overview
- HM01B0 camera → MAX78000 camera interface
- ESP8266 → UART pins
- MPU6050 → I2C (SDA/SCL)
- TEMT6000 → Analog input
- Buzzer → Controlled using 2N2222 transistor
- GPS → TX/RX serial communication
How the System Works
Step 1: Image Capture & Pre-Processing
The HM01B0 camera streams grayscale frames directly into the MAX78000’s convolution accelerator.
I perform basic preprocessing:
- Cropping the eye region
- Resizing to model input
Normalizing pixel values
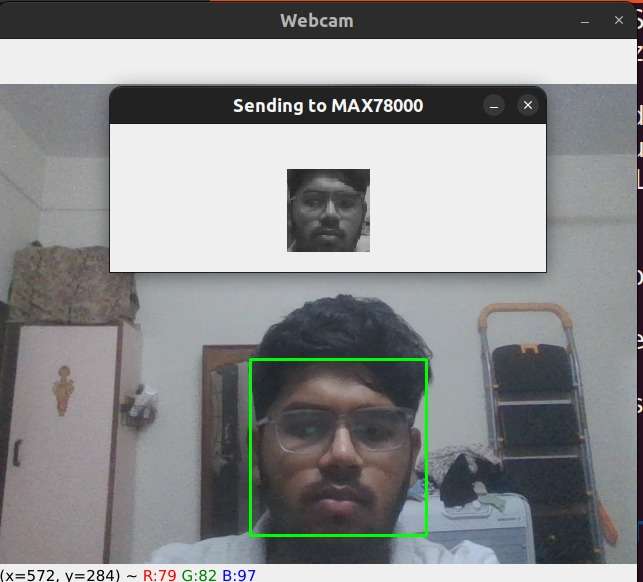
Step 2: CNN-Based Drowsiness Detection
I trained a custom AI85 CNN model and deployed it using Maxim’s toolchain.
The model is capable of detecting:
- Eye closures and blink duration
- Blink frequency
- Yawn patterns
Head tilt / distraction
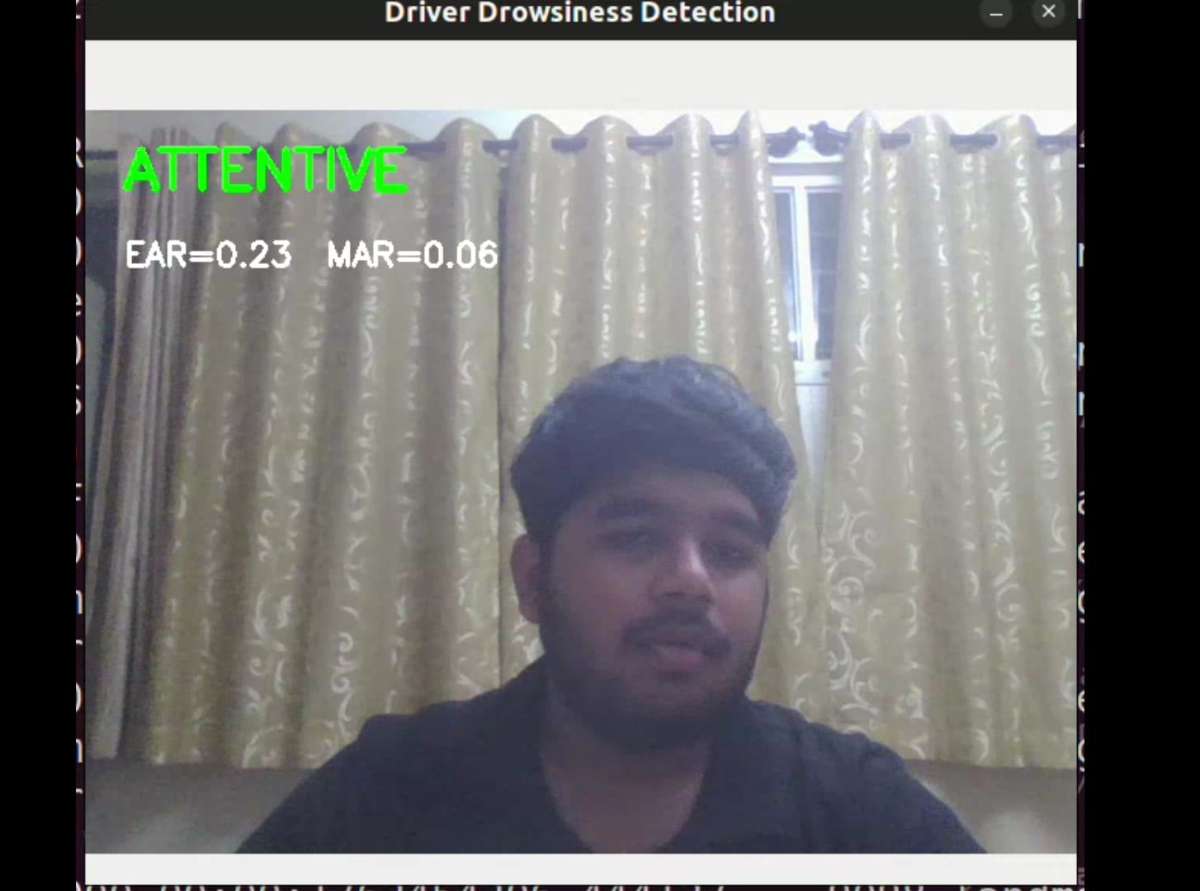
.jpeg)
All inference runs locally on the chip — no cloud, no delay, no privacy issues.
Step 3: Alert Logic
If the model detects drowsiness or distraction, the system triggers the buzzer and pushes an alert to Firebase.
if (eyeClosedTime > 2.0 || yawnDetected || headTilt > threshold) { buzzer_on(); send_alert_to_cloud(); }
Step 4 : Vehicle Sensor Fusion
SmartDash adds several vehicle-level sensors to give deeper context and reduce false positives:
MPU6050 — Vehicle Motion
Measures:
- Vehicle vibrations
- Sudden braking or harsh acceleration
- Road bumps
- Orientation changes
This helps the system understand vehicle dynamics and differentiate real events from camera noise.
mpu.getAcceleration(&ax, &ay, &az);
TEMT6000 — Vehicle Cabin Light Level
- Measures ambient brightness inside the vehicle
- Helps adjust camera thresholds
- Ensures detection works during night driving or tunnels
int lux = analogRead(LIGHT_PIN);
NEO-6M GPS — Location Logging
- Tags where fatigue events occur
- Helps fleet owners analyze risky routes
- Useful for long-haul trucks and taxis
lat = gps.location.lat(); lon = gps.location.lng();
DS3231 RTC — Accurate Event Timestamp
- Adds real-time date & time to every alert
- Ensures logs are correct even without internet
- Critical for fleet records and post-incident review
String timestamp = rtc.getDateTime();
Step 5 : IoT Dashboard (Firebase)
The ESP8266 sends real-time JSON packets:
here the link towards the dashborad : https://dhirendrag.github.io/vehicle-dashboard/
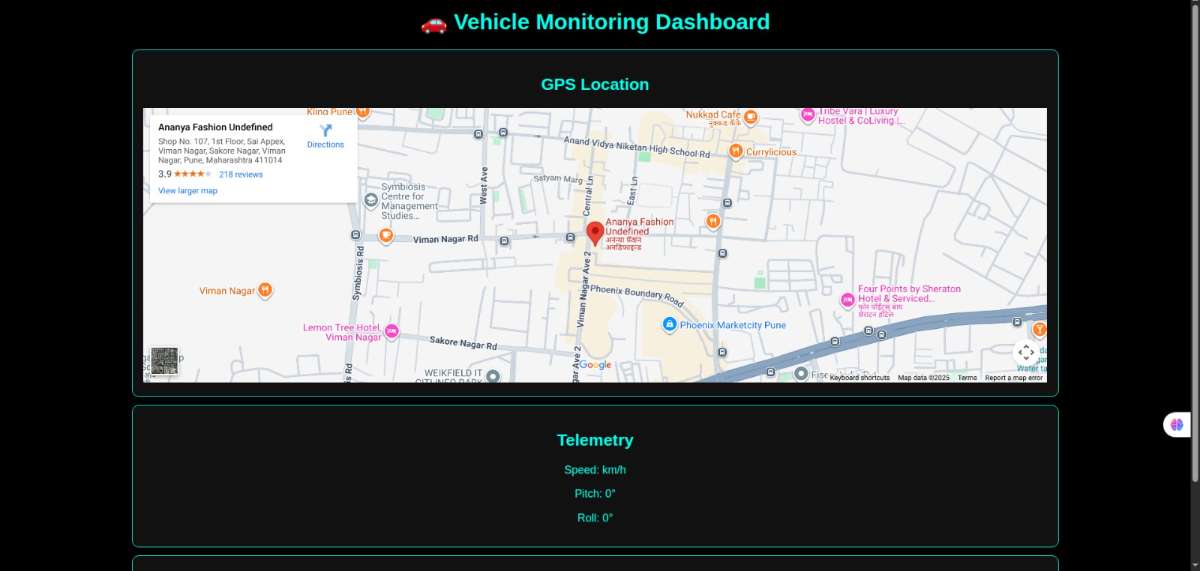
{ "drowsy": true, "blinkRate": 38, "tilt": 12, "light": 88, "timestamp": "2025-11-14 22:15" }
This allows remote monitoring through Firebase’s live dashboard.
Project Video
▶ https://youtu.be/oyReoTiQ5Pc
Bill of Materials (BOM)
DigiKey MyList
👉 https://www.digikey.in/en/mylists/list/6BHRP4QLOR
Components Used
- MAX78000FTHR Feather Board — 505-MAX78000FTHR#-ND
- HM01B0 Camera Module — 3367-HM01B0-MNA-00FT870-ND
- ESP8266 DevKitC — 1965-1002-ND
- NEO-M9N GPS — 672-NEO-M9N-00BTR-ND
- TEMT6000 Ambient Light Sensor — 751-1030-ND
- MPU6050 IMU — 1428-1069-1-ND
- 2N2222A + Buzzer
- Li-ion battery
- Jumper wires, connectors, breadboard
Software Structure
1.1 Dataset & Model Training (Compact)
Files:
train_model.py, test_model.py, convert_to_ai85.py
Functionality:
- Preprocess eye images (crop, normalize, augment)
- Train CNN for open/closed eye detection
- Evaluate accuracy + confusion matrix
- Convert trained model → AI85 format for MAX78000
Mini Snippets:
Training (train_model.py):
for img, lbl in train_loader: out = model(img.to(dev)) loss = crit(out, lbl.to(dev)) opt.zero_grad(); loss.backward(); opt.step() torch.save(model.state_dict(), "eye_model.pth")
Testing (test_model.py):
preds, labels = [], [] for img, lbl in test_loader: p = model(img).argmax(1) preds += p.tolist(); labels += lbl.tolist() print(confusion_matrix(labels, preds))
AI85 Conversion (convert_to_ai85.py):
ai8x.convert( state_dict=torch.load("eye_model.pth"), output_name="model_ai85.pth.tar" )
1.2 Live Detection (Compact)
Files:
live_drowsiness_webcam.py, live_model_def.py, ear_debug.py
Functionality:
- Capture webcam frames
- Extract eye region
- Run inference (open/closed)
- EAR debugging
- Send
"DROWSY"alert → ESP via UART
Mini Snippets:
Live detection (live_drowsiness_webcam.py):
pred = model.predict(eye) closed += 1 if pred=="closed" else 0 if closed > 15: uart.write(b"DROWSY")
Model (live_model_def.py):
class EyeCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): ... def forward(self,x): return self.fc2(...)
EAR (ear_debug.py):
ear = (dist(p1,p5)+dist(p2,p4)) / (2*dist(p0,p3)) print("EAR:", ear)
2. ESP8266
1. UART Handler
Receives "DROWSY" or "AWAKE" from MAX78000.
// uart_handler.cpp if (Serial2.available()) { String msg = Serial2.readStringUntil('\n'); if (msg == "DROWSY") drowsyFlag = true; }
2. MPU6050 Reading
Detect acceleration / jerks.
// sensor_manager.cpp mpu.getAcceleration(&ax, &ay, &az);
3. Light Sensor (TEMT6000)
int lux = analogRead(LIGHT_PIN);
4. GPS Reading (NEO-6M)
if (gps.encode(Serial1.read())) { lat = gps.location.lat(); lon = gps.location.lng(); }
Schematic
.png)
Results
- Real-time drowsiness detection
- Smooth CNN inference on MAX78000
- Live IoT alerts via Firebase
- Head-tilt and movement detection
- Works in low light due to adaptive sensing
Conclusion
SmartDash shows how low-power Edge AI can dramatically improve road safety by processing all intelligence locally on the device, without relying on cloud servers.
This enables:
- Instant response to drowsiness and distraction
- Full privacy, since no video leaves the vehicle
- Ultra-low bandwidth usage, suitable for remote areas
- High reliability, even when the network fails
When paired with a dashcam, SmartDash becomes a complete in-vehicle safety companion — capturing evidence while analyzing driver behavior in real time.
This makes the system suitable for:
- Commercial fleets
- Taxis & ride-sharing
- Long-haul trucking
- Corporate transport
- Personal vehicles
SmartDash is scalable, low-cost, and ready for real-world deployment.

.jpeg)